AC/DC
AC/DC
Learning objectives
- To define direct circuit and alternating circuit
- To observe the effect of a switch on an electrical circuit.
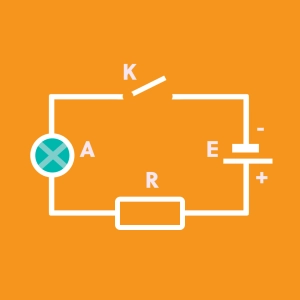
The direct current is characterised by an unidirectional flow of electrical charges. This means that the charges are always circulating in the same direction. This is the case in nearly all electronic circuits powered by batteries and also for some specific installations (trains). The material that functions in direct circuits is usually marked with the abbreviation "DC" (Direct Current).
The alternative current is characterised by an alternate flow of electrical charges. This means that the charges always come and go. This is the case in domestic circuits (houses, etc). The material that uses an alternative current is usually marked with the abbreviation "AC" (Alternating Current).

Discover EduMedia for free
The interactive encyclopedia that brings science and math to life in the classroom.
Over 1,000 resources